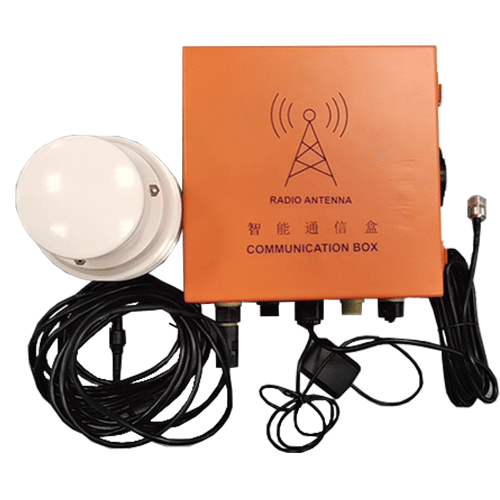
What are the functions of a solar tracker controller?
A solar tracker controller is an automatic control device used to control the charging of batteries from multiple solar cell arrays and to supply power to solar inverters from the batteries in a solar power generation system.
The solar controller uses a high-speed CPU microprocessor and a high-precision A/D converter, making it a microcomputer data acquisition and monitoring control system. It can quickly and accurately collect the current working status of the photovoltaic system and accumulate historical data for evaluating the design rationality and component quality reliability of the PV system.
In addition, the solar tracker controller also has a serial communication data transmission function, which can centrally manage and remotely control multiple photovoltaic system substations.
Through the use of innovative maximum power tracking technology, the solar controller can guarantee maximum efficiency of the solar array working throughout the day and under all weather conditions. This can increase the working efficiency of photovoltaic components by 30% (with an average efficiency increase of 10% - 25%).
The solar tracker controller also has a search function that searches for the absolute maximum power output point every 2 hours within the entire working voltage range of the solar panel. The temperature-compensated three-stage I-U curve charging control can significantly extend the life of the battery. The solar controller is suitable for independent 12V or 24V systems, which can greatly reduce the cost of the entire system.
What is the role of a solar tracker controller?
Power regulation function.
Communication functions, simple indication functions, and protocol communication functions.
Complete protection functions: electrical protection, reverse connection protection, short circuit protection, and overcurrent protection.
What is the charge and discharge protection of a solar tracker controller?
Direct charging protection point voltage: Direct charging, also known as emergency charging, is a fast charging method. It generally uses a large current and relatively high voltage to charge the battery when the battery voltage is low. The direct charging protection point voltage is generally the "overcharge protection point" voltage, and the battery terminal voltage cannot be higher than this protection point during charging, otherwise it will cause overcharging and damage to the battery.
Equal charge control point voltage: After direct charging is completed, the battery is generally left idle by the charge-discharge controller for a period of time. When the voltage drops to the "recovery voltage" value, it enters the equal charge state.
Floating charge control point voltage: After equal charging is completed, the battery is generally left idle for a period of time to allow its terminal voltage to naturally drop. When the voltage drops to the "maintenance voltage" point, it enters the floating charge state. Currently, PWM (pulse width modulation) is commonly used, similar to "trickle charging" (i.e. small current charging). The battery voltage is charged a little when it is low, to avoid continuous temperature rise inside the battery, which is beneficial to the battery as the internal temperature has a great influence on charging and discharging.
Overdischarge protection termination voltage: For safety reasons, 0.3V is generally added to the overdischarge protection point voltage of a 12V battery for temperature compensation or control circuit zero drift calibration. Thus, the overdischarge protection point voltage of a 12V battery is 11.10V, and the overdischarge protection point voltage of a 24V system is 22.20V.
 English
English  中文
中文